What Happens to the Energy That the Ground Absorbs in the Form of Visible Sunlight?
What is the absorption and reflection of sunlight?
The Sunday provides the Earth with almost of its energy. Today, well-nigh 71% of the sunlight that reaches the Earth is absorbed by its surface and temper. Absorption of sunlight causes the molecules of the object or surface it strikes to vibrate faster, increasing its temperature. This energy is then re-radiated by the Earth as longwave, infrared radiations, also known as heat. The more than sunlight a surface absorbs, the warmer it gets, and the more energy it re-radiates as oestrus. This re-radiated heat is then captivated and re-radiated by greenhouse gases and clouds, and warm the atmosphere through the greenhouse effect.
Globe's surfaces are better at absorbing solar radiation than air, particularly surfaces that are dark in color. You can feel this on a cold winter mean solar day when the sunshine warms your face up and the air around yous remains cold. Your skin and your clothes also absorb solar radiations and convert it to heat. If you vesture a black jacket, it will absorb more radiation and make you feel warmer than if yous habiliment a white or light-colored jacket. Similarly, Earth's dissimilar surfaces and parts of the atmosphere absorb solar radiation at different rates.
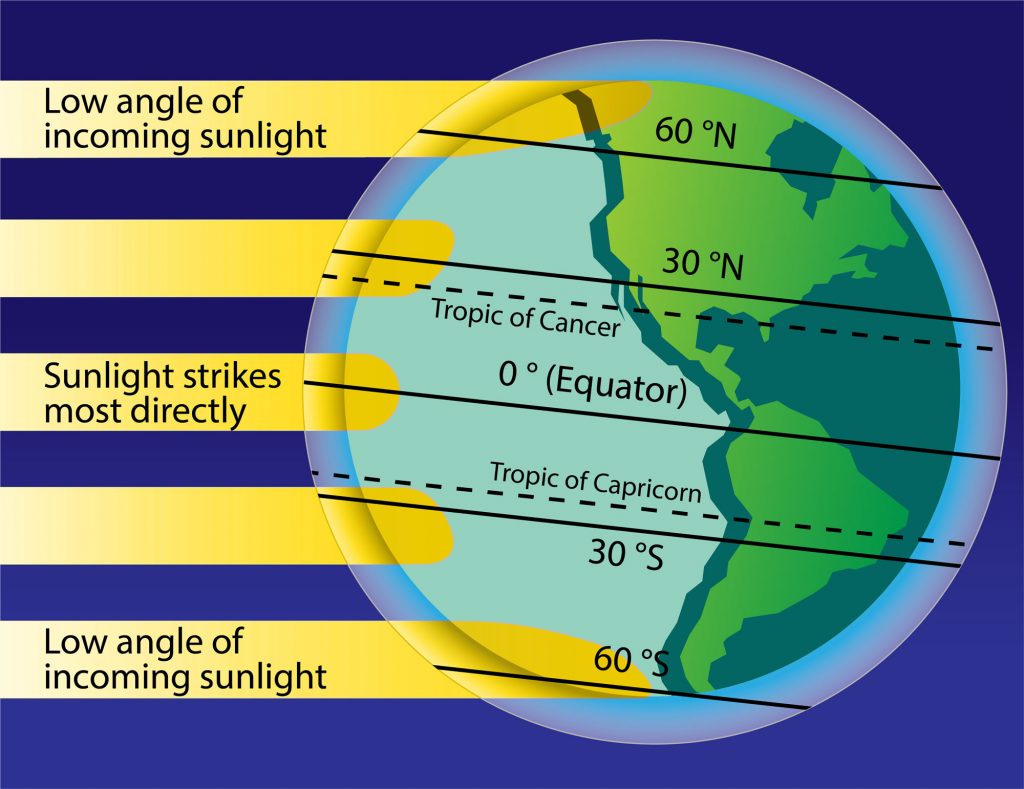
The Earth is unevenly heated because it is a sphere.
Considering Earth is a sphere, not all part of the Earth receives the aforementioned amount of solar radiation. More solar radiation is received and absorbed near the equator than at the poles. Nigh the equator, the Sun'due south rays strike the Earth most directly, while at the poles the rays strike at a steep angle. This ways that less solar radiation is absorbed per square cm (or inch) of surface expanse at college latitudes than at lower latitudes, and that the tropics are warmer than the poles. This temperature difference shapes global atmospheric and ocean apportionment patterns. Additionally, Earth's tilt affects how much sunlight is received and absorbed by different parts of the Earth at various times of the year, and is why we experience the seasons. The amount of solar radiations received and absorbed also influences process in the biosphere by directly affecting plants and other organisms that photosynthesize and are the primary food source in most ecosystems (see species interactions).
If calorie-free is non captivated past a surface, it is mostly reflected. Reflection occurs when incoming solar radiation bounces dorsum from an object or surface that it strikes in the temper, on land, or h2o, and is not transformed into heat. The proportion of incoming solar radiations that is reflected by the World is known equally its albedo. Overall, Earth reflects nearly 29% of the incoming solar radiation, and therefore, we say the World'south average albedo is 0.29.
Snow and ice, airborne particles, and sure gases have loftier albedos and reverberate different amounts of sunlight back into infinite. Low, thick clouds are reflective and can cake sunlight from reaching the Earth'due south surface, while high, sparse clouds can contribute to the greenhouse effect.
The proportion of sunlight that'southward reflected vs. captivated, the re-radiations of heat, and the intensity of the greenhouse effect influence the amount of free energy in the Earth system and global processes such every bit the water bicycle and atmospheric and ocean circulation.
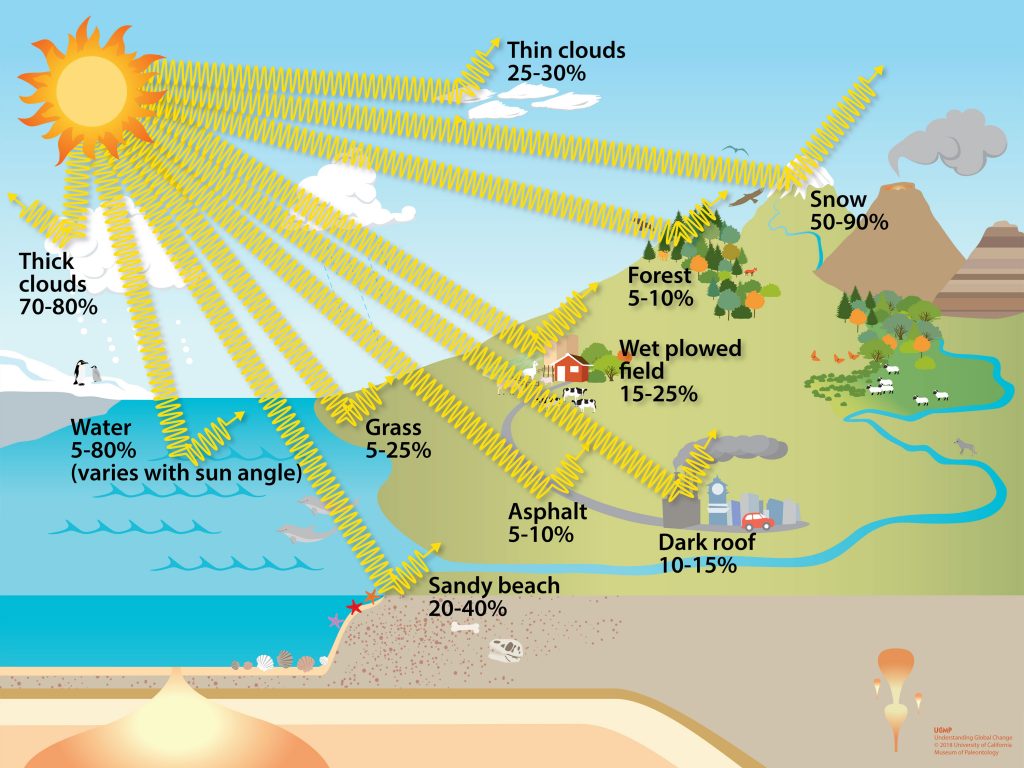
This diagram shows the percentage of sunlight that is reflected by different Earth surfaces or clouds.
Earth arrangement models about the absorption and reflection of sunlight
This Globe system model is one mode to correspond the essential processes and interactions related to the absorption and reflection of sunlight. Hover over the icons for brief explanations; click on the icons to acquire more about each topic. Download the Earth system models on this folio.
This model shows some of the changes to World's surface and atmosphere that can touch the amount of sunlight that is absorbed or reflected. These changes influence the corporeality of oestrus that is re-radiated, and can too greatly influence the biosphere past altering the corporeality of sunlight available for photosynthesis.
How human activities influence the assimilation and reflection of sunlight
The Earth organisation model below includes some of the ways that human activities straight affect the corporeality of sunlight that is absorbed and reflected by Globe's surface. The development and spread of urban areas, especially using cobblestone and other dark colored materials, can dramatically increase the absorptivity of the surface. This creates urban heat islands, where cities experience higher temperatures than surrounding areas. Hover over or click on the icons to learn more about these human causes of change and how they influence the absorption and reflection of sunlight.
The World system model below includes boosted means that human activities directly affect the amount of sunlight that is captivated and reflected by Earth'southward temper. Hover over or click on the icons to learn more nearly these homo causes of change and how they influence the assimilation and reflection of sunlight.
The World system model below shows how human pollutants and waste material bear on the ozone layer and the amount of ultraviolet sunlight that is absorbed past Globe's upper temper (the stratosphere). Hover over or click on the icons to larn more about these human causes of change and how they influence the absorption and reflection of sunlight.
Explore the Earth System
Click the icons and bolded terms (e.g. re-radiation of heat, airborne particles, etc.) on this page to larn more nigh these process and phenomena. Alternatively, explore the Understanding Global Change Infographic and notice new topics that are of interest and/or locally relevant to you.
To learn more most pedagogy the assimilation and reflection of sunlight, visit the Teaching Resources page.
Links to Learn More
- Earth's Energy Budget
- Measuring World's Albedo via Satellite/ CERES
- A cursory description of NASA's "Clouds and the Globe's Radiant Energy Arrangement" (CERES) satellite instruments
- Woods Pigsty Oceanographic Institution: How tiny plants help brand clouds
- Earth's Albedo and Global Warming
- NOAA Science on a Sphere, Aerosols: Blackness carbon and sulfate
- Ozone: What is it, and why do we care about information technology?
Source: https://ugc.berkeley.edu/background-content/reflection-absorption-sunlight/
0 Response to "What Happens to the Energy That the Ground Absorbs in the Form of Visible Sunlight?"
Post a Comment